Python轻松实现EXCEL转XML
编者按:本文来自微信公众号“51Testing软件测试网”(ID:testing51testing),作者:快乐至上,36氪经授权发布。
出品|51Testing软件测试网
本文将结合作者项目实践,介绍如何将EXCEL文件通过Python转换为XML,以方便导入到Testlink中(Testlink仅支持XML文件的导入),并且顺便介绍一下Python常见的错误及解决方案,希望对大家有所帮助。
声明:文中转换工具涉及的代码是借鉴了其他帖子上的一部代码,结合本文作者项目的实际情况,编写而成。
输出EXCEL格式的测试用例文件
1
模板
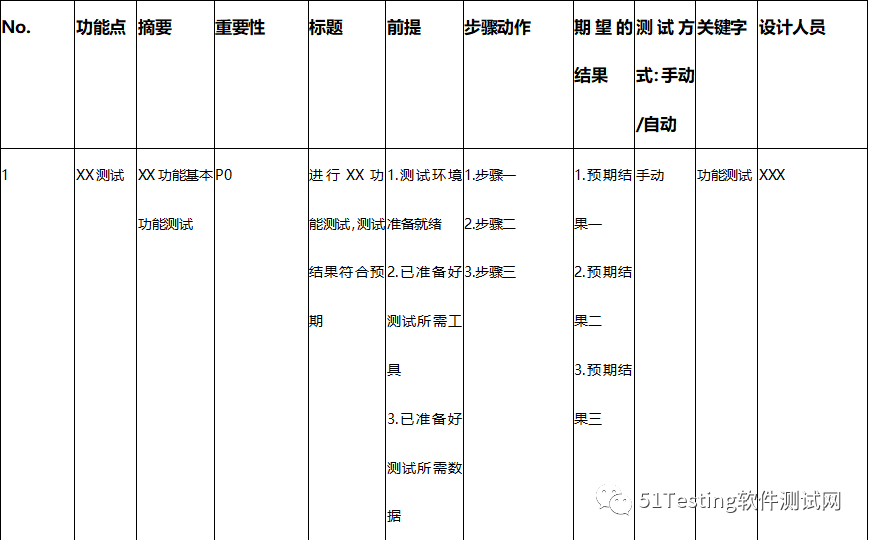
测试用例使用如下模板输出,保存为XXX.xlsx文件,例如命名case.xlsx。
2
部分字段解释
功能点
一般EXCEL文件的一个Sheet页代表一个模块,在一个模块内部分为多个功能点,通过一个或多个测试用例对每个功能点进行一一覆盖,功能点字段就是对模块进行结构化划分的。
测试方式
该字段用以标识测试方式,是手工测试还是自动化测试,方便日后识别哪些用例是自动化实现的用例。
关键字
这个字段可以多种用途,例如用于识别产品形态,识别用例输出版本,或者用于识别质量属性,都是可以的。
作者项目中,是用于识别质量属性的,例如功能测试、性能测试、易用性测试等等。
重要性
填写P0/P1/P2,表示三个用例级别:高、中、低。
设计人员
该字段是用来标识用例的作者的,用于方便可追溯性或用例维护。
安装Python 3
由于本文中的EXCEL转换为XML的工具是用Python语言写的,所以,首先需要安装Python运行环境,本文中用的是3.6.2。
若已经安装了Python 3,则跳过此步骤。
1
下载安装Python
Python3可以去网上免费下载安装,地址为:
https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.6.2/python-3.6.2-amd64.exe
2
配置运行环境
安装完Python后,配置环境变量。
我的电脑-》属性-》高级系统设置-》高级-》环境变量,在用户变量部分,找到变量名为path的,点击编辑、新建,将Python安装目录及pip所在目录都添加到环境变量表中,此例中为:\Python3d6\Python36\和F:\Python3d6\Python36\Scripts\。
具体的步骤在本文中就不赘述了,需要的可以自己去网上找。
3
调试Python及pip
配置好环境变量后,就在CMD下运行Python和pip,安装py脚本中涉及的Python库。
但是作者在调试过程中,曾经遇到了如下的几个问题,供大家参考。
错误一
现象:
Cmd命令行下,敲pip报错,敲Python正常,具体信息如下:
C:\Users\Administrator>pipFatal error in launcher: Unable to create process using '"c:\python36\python3.exe" "F:\Python3d6\Python36\Scripts\pip.exe" ': ???????????C:\Users\Administrator>python3Python 3.6.2 (v3.6.2:5fd33b5, Jul 8 2017, 04:57:36) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
前置条件:
1)Python安装目录为F:\Python3d6\Python36\;
2)已经将F:\Python3d6\Python36\和F:\Python3d6\Python36\Scripts\配置到环境变量中。
排查思路:
第一步,经初步判断,感觉是路径有问题。
随后,将安装路径改为F:\Python36\,即将“Python3d6”这层文件夹去掉,并重新配置环境变量。
现象:
Cmd命令行下,敲Python正常,敲pip仍然后报错。
报错如下:
C:\Users\Administrator>pip install pywin32Fatal error in launcher: Unable to create process using '"c:\python36\python3.exe" "F:\Python36\Scripts\pip.exe" install pywin32': ???????????
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
第二步,排除环境变量配置问题。
cd到安装目录下,执行pip,仍然报错。具体报错信息如下:
F:\Python36\Scripts>pip install pywin32Fatal error in launcher: Unable to create process using '"c:\python36\python3.exe" "F:\Python36\Scripts\pip.exe" install pywin32': ???????????
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
第三步,尝试把Python整个文件夹从F盘移动到C盘,然后修改好环境变量。
执行pip,没有报错,问题搞定,打印信息如下:
C:\Users\Administrator>pipUsage: pip <command> [options]Commands: install Install packages. download Download packages. uninstall Uninstall packages.......
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
错误二
现象:
Python运行.py文件报错 :NameError name 'reload' is not defined。
相关代码:
import sysreload(sys)sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")
原因:
setdefaultencoding是Python2的sys库里边的函数,Python3的sys库里面已经没有 setdefaultencoding() 函数,并且Python3系统默认使用的就是utf-8编码。
解决方案:
将sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8")代码整行去掉即可。
错误三
现象:调用print函数出错,具体报错信息如下:
C:\Users\Administrator>python3 F:\case\operate.py File "F:\case\operate.py", line 46 print 'str=', str ^SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
原因:
python2.X版本与python3.X版本输出方式不同造成的。
解决方案:
Print函数后面加上括号()。
4
Python2代码与Python3代码不兼容
其实将Python代码用Python3执行,很多问题都是由于Python2版本和Python版本代码不兼容导致的。
下面以实际的例子,介绍一种Python2代码转换成Python3代码的方法。
假设:
Python2.X到Python3.X转换文件2to3.py的路径为C:\Python36\Tools\scripts。
待转换的文件operate.py的路径为D:\python2to3。
CMD下执行如下命令,即可将该Python2文件转换为Python3文件:
python3 C:\Python36\Tools\scripts\2to3.py -w D:\python2to3\operate.py
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
出现如下打印说明转换过程成功:
C:\Users\Administrator>python3 C:\Python36\Tools\scripts\2to3.py -w D:\python2to3\operate.pyRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: bufferRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: idiomsRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: set_literalRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: ws_commaRefactoringTool: Refactored D:\python2to3\operate.py--- D:\python2to3\operate.py (original)+++ D:\python2to3\operate.py (refactored)@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@ # coding:utf-8 import os,re,xlrd import sys-reload(sys)+import imp+imp.reload(sys) sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8") from easy_excel import easy_excel@@ -43,7 +44,7 @@ def actions_add_div(str): if str: new_action_str=""- print 'str=', str+ print('str=', str) for str_index in str.split('\n'): newline=str_index + " " + "</div> " + "<div>" + " " + "</p> " + "<p>" new_action_str+=newline@@ -122,16 +123,16 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":- print os.path.abspath('.')+ print(os.path.abspath('.')) excellist=[] #列出当前目录下的所有.xml文件 for fullname in iterbrowse(os.path.abspath('.')):- print fullname+ print(fullname) obj1=re.compile(r'([\W\w]*)(\.xlsx)$') for m in obj1.finditer(fullname):- print m.group()+ print(m.group()) excellist.append(m.group())- print excellist+ print(excellist) for fileName in excellist: fileName=fileName.split('\\')[-1] file_data = xlrd.open_workbook(fileName)@@ -139,12 +140,12 @@ sheetList=[] for index in range(sheetnum): sheet_name=file_data.sheets()[index].name- print sheet_name+ print(sheet_name) sheetList.append(sheet_name)- print sheetList+ print(sheetList) for sheetName in sheetList: test = operate(fileName, sheetName) test.xlsx_to_dic(sheetName) test.dic_to_xml(fileName, sheetName)- print "Convert success!"+ print("Convert success!") os.system('pause')RefactoringTool: Files that were modified:RefactoringTool: D:\python2to3\operate.py
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
从日志中可以看出,转换过程中,对哪些行进行了修改一目了然。
如果某Python文件不需要转换,则会出现如下的打印:
C:\Users\Administrator>python3 C:\Python36\Tools\scripts\2to3.py -w D:\python2to3\operate.pyRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: bufferRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: idiomsRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: set_literalRefactoringTool: Skipping optional fixer: ws_commaRefactoringTool: No changes to D:\python2to3\operate.pyRefactoringTool: Files that need to be modified:RefactoringTool: D:\python2to3\operate.py
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
将EXCEL转换为XML
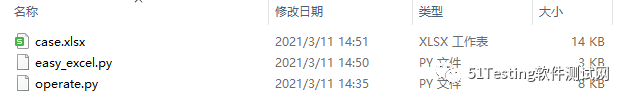
安装好Python库后,将用例表格与脚本放入同目录(脚本代码在文末),如下:
注意:用例表格的名称需用英文,不要含有中文。
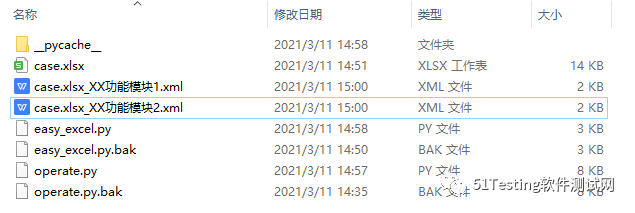
cd到表格和脚本所在目录,然后运行 operate.py 文件,打印如下:
D:\python2to3>python3 operate.pyD:\python2to3D:\python2to3\case.xlsxD:\python2to3\case.xlsxD:\python2to3\easy_excel.pyD:\python2to3\easy_excel.py.bakD:\python2to3\operate.pyD:\python2to3\operate.py.bakD:\python2to3\__pycache__\easy_excel.cpython-36.pyc['D:\\python2to3\\case.xlsx']XX功能模块1XX功能模块2['XX功能模块1', 'XX功能模块2']('str=', '1.步骤一\n2.步骤二\n3.步骤三')('str=', '1.步骤一\n2.步骤二\n3.步骤三')Convert success!请按任意键继续. . .
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
转换成功,按照EXCEL的sheet页输出两个XML文件:case.xlsx_XX功能模块1.xml和case.xlsx_XX功能模块2.xml,可以用来导入到Testlink用例管理系统中。
代码
1
easy_excel.py
# coding=utf-8from xml.etree import ElementTreefrom win32com.client import Dispatchimport win32com.clientimport osimport sysimport impimp.reload(sys)class easy_excel: def __init__(self, filename=None): self.xlApp = win32com.client.Dispatch('Excel.Application') if filename: self.filename = os.getcwd() + "\\" + filename # self.xlApp.Visible=True self.xlBook = self.xlApp.Workbooks.Open(self.filename) else: # self.xlApp.Visible=True self.xlBook = self.xlApp.Workbooks.Add() self.filename = '' def save(self, newfilename=None): if newfilename: self.filename = os.getcwd() + "\\" + newfilename # if os.path.exists(self.filename): # os.remove(self.filename) self.xlBook.SaveAs(self.filename) else: self.xlBook.Save() def close(self): self.xlBook.Close(SaveChanges=0) self.xlApp.Quit() def getCell(self, sheet, row, col): sht = self.xlBook.Worksheets(sheet) return sht.Cells(row, col).Value def setCell(self, sheet, row, col, value): sht = self.xlBook.Worksheets(sheet) sht.Cells(row, col).Value = value # 设置居中 sht.Cells(row, col).HorizontalAlignment = 3 sht.Rows(row).WrapText = True def mergeCells(self, sheet, row1, col1, row2, col2): start_coloum = int(dic_config["start_coloum"]) # 如果这列不存在就不合并单元格 if col2 != start_coloum - 1: sht = self.xlBook.Worksheets(sheet) sht.Range(sht.Cells(row1, col1), sht.Cells(row2, col2)).Merge() # else: # print 'Merge cells coloum %s failed!' %col2 def setBorder(self, sheet, row, col): sht = self.xlBook.Worksheets(sheet) sht.Cells(row, col).Borders.LineStyle = 1 def set_col_width(self, sheet, start, end, length): start += 96 end += 96 msg = chr(start) + ":" + chr(end) # print msg sht = self.xlBook.Worksheets(sheet) sht.Columns(msg.upper()).ColumnWidth = length
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
2
operate.py
# coding:utf-8import os,re,xlrdimport sysimport impimp.reload(sys)from easy_excel import easy_excelclass operate(): def __init__(self, ExcelFileName, SheetName): self.excelFile = ExcelFileName self.excelSheet = SheetName self.temp = easy_excel(self.excelFile) self.dic_testlink = {} self.row_flag = 2 self.testsuite = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, 2, 2) #print 'self.testsuite=',self.testsuite self.dic_testlink[self.testsuite] = {"node_order": "13", "details": "", "testcase": []} self.content = "" self.content_list = [] def xlsx_to_dic(self, SheetName): while True: testcase = {"name": "", "node_order": "100", "externalid": "", "version": "1", "summary": "", "preconditions": "", "execution_type": "1", "importance": "3", "steps": [], "keywords": "P1", "author":""} testcase["name"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 5) testcase["summary"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 3) testcase["preconditions"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 6) execution_type = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 9) testcase["keywords"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 10) testcase["author"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 11) if execution_type == "自动": testcase["execution_type"] = 2 step_number = 1 importance = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 4) if importance == "基本功能" or importance == "P1": testcase["importance"]="2" elif importance == "拓展" or importance == "P2": testcase["importance"] = "1" while True: step = {"step_number": "", "actions": "", "expectedresults": "", "execution_type": ""} step["step_number"] = step_number step["actions"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 7) def actions_add_div(str): if str: new_action_str="" print(('str=', str)) for str_index in str.split('\n'): newline=str_index + " " + "</div> " + "<div>" + " " + "</p> " + "<p>" new_action_str+=newline return new_action_str[:-21] step["actions"]=actions_add_div(step["actions"]) step["expectedresults"] = self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 8) testcase["steps"].append(step) step_number += 1 self.row_flag += 1 if self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 1) is not None or self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 5) is None: break # print testcase self.dic_testlink[self.testsuite]["testcase"].append(testcase) # print self.row_flag if self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag, 5) is None and self.temp.getCell(self.excelSheet, self.row_flag + 1, 5) is None: break self.temp.close() # print self.dic_testlink def content_to_xml(self, key, value=None): if key == 'step_number' or key == 'execution_type' or key == 'node_order' or key == 'externalid' or key == 'version' or key == 'importance': return "<" + str(key) + "><![CDATA[" + str(value) + "]]></" + str(key) + ">" elif key == 'actions' or key == 'expectedresults' or key == 'summary' or key == 'preconditions': return "<" + str(key) + "><![CDATA[<div> " + str(value) + "</div> ]]></" + str(key) + ">" elif key == 'keywords': return '<keywords><keyword name="' + str(value) + '"><notes><![CDATA[ aaaa ]]></notes></keyword></keywords>' elif key == 'name': return '<testcase name="' + str(value) + '">' elif key == 'author': return '<custom_fields><custom_field><name><![CDATA[设计人员]]></name><value><![CDATA[%s]]></value></custom_field></custom_fields>' % str(value) else: return '##########' def dic_to_xml(self, ExcelFileName, SheetName): testcase_list = self.dic_testlink[self.testsuite]["testcase"] for testcase in testcase_list: for step in testcase["steps"]: self.content += "<step>" self.content += self.content_to_xml("step_number", step["step_number"]) self.content += self.content_to_xml("actions", step["actions"]) self.content += self.content_to_xml("expectedresults", step["expectedresults"]) self.content += self.content_to_xml("execution_type", step["execution_type"]) self.content += "</step>" self.content = "<steps>" + self.content + "</steps>" self.content = self.content_to_xml("importance", testcase["importance"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("execution_type", testcase["execution_type"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("preconditions", testcase["preconditions"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("summary", testcase["summary"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("version", testcase["version"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("externalid", testcase["externalid"]) + self.content self.content = self.content_to_xml("node_order", testcase["node_order"]) + self.content self.content = self.content + self.content_to_xml("keywords", testcase["keywords"]) self.content = self.content_to_xml("name", testcase["name"]) + self.content self.content = self.content + self.content_to_xml("author", testcase["author"]) self.content = self.content + "</testcase>" self.content_list.append(self.content) self.content = "" self.content = "".join(self.content_list) self.content = '<testsuite name="' + self.testsuite + '">' + self.content + "</testsuite>" self.content = '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>' + self.content self.write_to_file(ExcelFileName, SheetName) def write_to_file(self, ExcelFileName, SheetName): xmlFileName = ExcelFileName + '_' + SheetName + '.xml' cp = open(xmlFileName, "w") cp.write(self.content) cp.close() #遍历某个文件目录下的所有文件名称def iterbrowse(path): for home, dirs, files in os.walk(path): for filename in files: yield os.path.join(home, filename) if __name__ == "__main__": print((os.path.abspath('.'))) excellist=[] #列出当前目录下的所有.xml文件 for fullname in iterbrowse(os.path.abspath('.')): print(fullname) obj1=re.compile(r'([\W\w]*)(\.xlsx)$') for m in obj1.finditer(fullname): print((m.group())) excellist.append(m.group()) print(excellist) for fileName in excellist: fileName=fileName.split('\\')[-1] file_data = xlrd.open_workbook(fileName) sheetnum=len(file_data.sheets()) sheetList=[] for index in range(sheetnum): sheet_name=file_data.sheets()[index].name print(sheet_name) sheetList.append(sheet_name) print(sheetList) for sheetName in sheetList: test = operate(fileName, sheetName) test.xlsx_to_dic(sheetName) test.dic_to_xml(fileName, sheetName) print("Convert success!") os.system('pause')
(左右滑动查看完整代码)
End
推荐阅读
点击阅读☞接口自动化核心知识点浓缩,为面试加分!
点击阅读☞惊呆,原来QA需要具备这么多能力
点击阅读☞211本科大佬的真实面试经历:测试人要不要去外包公司?
点击阅读☞2020年应聘华为测试岗三轮面试经历分享
戳 “阅读原文”一起来充电吧!